Thursday, March 21, 2013
Today's Class 3/21/13
Today in class we worked on our presentations. Mine Cameron's and Maddie's is about the Death of Alexander the Great. I wrote about how he was buried and what happened after he died. Maddie wrote about possible causes of death. And Cameron added pictures. I learned that when he was buried that he was laid in a gold tub filled with honey. Also he had a child on the way when he died and if it was a male he would grow up and be king.
Wednesday, March 20, 2013
Today's Class 3/20/13
In class today we went over the home work from Monday and I think i did petty well on it. Also we were put in groups for a project that we are doing on Alexander the Great. Olivia and I really really wanted to be in the same group but sadly Mr. Schick chose the groups. I am in a group with Cameron and Maddie. Our presentation is on the Death of Alexander the Great. The title of it is THE GREAT DEATH OF ALEXANDER THE GREAT!! I came up with hat name.
Tuesday, March 19, 2013
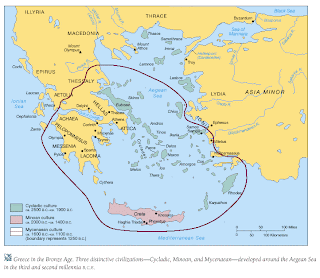
300 BC / Map / Athens in the War / 359 BC
By 300 BC the Greeks reached a new
era witch was the Hellenistic era. During which they were the leading
international culture but their way of life was also influence by the people
that ruled. But the Greeks themselves had evolved from a barbarian people on
civilizations northwest edge. They did this to become a more dominant
civilization.
During the
war it was hard for either side to strike a decisive blow until the Athenians
naval looses in Sicily. The also ran out of money and supplies from the still
mighty Persian Empire. This enabled Sparta to build a navy the defeated Athens.
But Athens soon formed an alliance of city-states to go over to the offensive,
which most of the Greek city-states on the Aegean coast and islands eventually
joined. Money was given to build triremes that went under Athens commands. They
then gained command over several hundred ships. After the Persians excepted
defeat the Athens forced its allies to keep sending money. The city-states of
Greece were provoked by the Athenians. The city- states were usually run by
oligarchies, but Athens insisted on being run by a Democracy. The course of the
war, the Athenians, under the guidance of Pericles, at first showed caution and
sound strategy. The Spartans, unbeatable on the battlefield but not equipped
for siege warfare, often raided Attica but could not capture the city itself or
cut its link to the sea.
In 359 BC, Macedonia came under the
rule of King Philip II, a ruler of broad vision who was determined to gain
control of the city-states and to lead the Greeks and Macedonians in a united force
against barbarian peoples to the north, He strengthened his army and adopted
Greek phalanx tactics, improving the weapons of his hoplites, and building up a
stronger cavalry force than any city-state possessed.
Sunday, March 17, 2013
Notes For Chapter 4Test
IMPORTANT DATES: In a sentence or two,
describe what important or historical event took place on the following dates:
1600 – 1200 BC: Mycenean civilization
1150 – 750 BC- The Dark Ages
776 BC-Olympic games
750 – 700 BC-Homer wrote the Iliad and the Odyssey
508 BC-Athens takes over rulers and Isagaoris was involved
and they turned to Cleisthenes
490 BC-Philipides runs from Persian attack to Marathon from
Athens
480 BC-triremes were built and Athens beat the Persians in
the Strait of Salames
447 – 438 BC-Parthenon was built
431 – 404 BC-Athens goes to war with Sparta (Peloponnesian)
Paraclese died due to plague
399 BC-Socrates dies
336 BC-Alexander the Great created his empire
MEN, WOMEN, GODS AND GODDESSES YOU SHOULD KNOW: In
one or two sentences, describe what is significant about the following people
(or immortals):
Homer- author of the Iliad and the Odyssey
Odysseus- the
main character in Odyssey, took 10 years to get home from the Trojan War
Zeus- father of the Gods
Athena- patron of Athens, Goddess of Wisdom
Draco- helped make the Greek laws
Solon- law maker, statesmen and poet
Pisistratus- came into Athens with Athena and took
over and turned to the commoners
Cleisthenes- was an aristocrat and fought Persia but
got thrown out
Darius (the Great)- king of Persia at time of the
battle of Marathon
Xerxes- Darius’ son and wanted to get revenge on
Athens
Pheidippides- ran the marathon and ran to Sparta but
they said no
Themistocles- a normal guy who told the people of
Athens to build 200 triremes with the silver they had found because they were
going to go to war with the Persians; he was later ostracized
Pericles- ruler of Athens, built the Parthenon, and in
431 B.C. came up with a plan to go to war with Sparta and to hide behind massive
walls while they were to attack at sea. he died in 429.B.C due to the plague
after 6 months with the disease
Socrates- a man who invented the idea of
deciding things on good and bad, to ask questions in order to get a response to your own
question, and replacing the Gods with logic. he was killed in 399 B.C due to
hemlock after being accused of corrupting Athens youth and undermining state
religion HE SAID: "the unexamined life isn't worth living"
LOCATION, LOCATION, LOCATION: Be
able to locate the following on a map:
Athens
Sparta
Peloponnesus
Ionia
GREEK POLITICAL STRUCTURES: Describe
these political institutions:
Monarchy- have a king(if he dies, the son takes
over)
Democracy-everyone making a vote on an issue
Oligarchy-a group making decisions usually
elders
Aristocracy- the aristocrats having all the
power
PERICLES’ THREE GOALS FOR ATHENS: build
the parthanon, wanted to go to war with sparta to be the greatest city state in
Greece, and
GREEK ART: Identify and describe examples
in these fields:
Sculpture-they created figureens out of different
materials like marble or clay like the 40 foot high gold and ivory statue of
Athena in the Parthenon
Architecture- building things like buildings and
structures like the Parthenon to show how great and talented Athens
was
Drama (tragedy and comedy)-the first theater was in
the acropolis and civilians went twice a year for festivels and to watch plays;
tragedies told stories of great men falling from great heights and loosing everything.


Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)